Mike dunning dorling kindersle getty images.
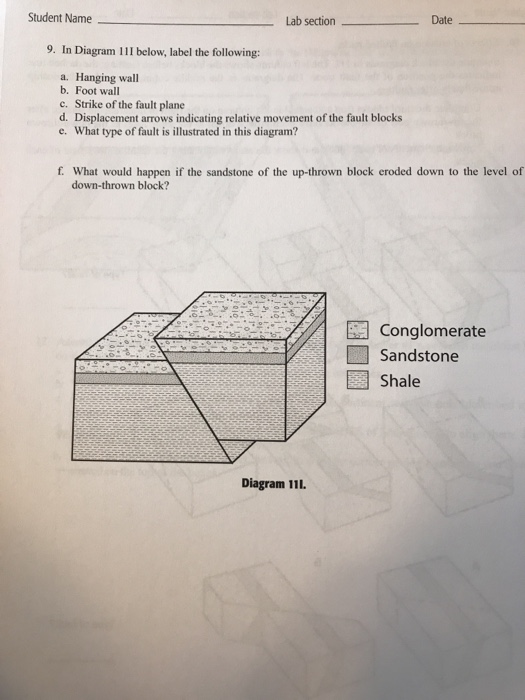
Hanging wall footwall hanging wall up.
On each photo draw arrows showing the relative movement on each side of the fault.
In a reverse fault the hanging wall right slides over the footwall left due to compressional forces.
The underlying block of a fault having an inclined fault plane.
The mass of rock underlying a mineral deposit in a mine.
The terminology of normal and reverse comes from coal mining in england where normal faults are the most common.
Reverse faults indicate compressive shortening of the crust.
Cirques tarns u shaped valleys arêtes and horns.
In an ideal cirque the headwall is semicircular in plan view.
Identify the type of fault illustrated by each photo and describe the type of stress that produced it.
A reverse fault is the opposite of a normal fault the hanging wall moves up relative to the footwall.
The forces creating reverse faults are compressional pushing the sides together.
In a non vertical fault where the fault plane dips the footwall is the section of the fault that lies under the fault while the hanging wall lies over the fault the names come about from the.
The dip of a reverse fault is relatively steep greater than 45.
Reverse faults form when the hanging wall moves up.
Hanging wall definition the underside of the wall rock overlying a vein or bed of ore.
Label the hanging wall block and the footwall block on each of the faults illustrated in figure 1.
Draw a normal and reverse fault label the hanging wall and footwall for each also show how they move for each fault.
When the hanging wall moves up in relative to the footwall it is called a fault.
When the hanging wall moves down in relative to the footwall it is called a fault.
These usually occur when tectonic forces cause tension that pulls rocks apart.
Footwall synonyms footwall pronunciation footwall translation english dictionary definition of footwall.
An arcuate cliff called the headwall.